Simple Search
Search by a single field and value
Advanced Search
Search using multiple criteria simultaneously
Array Search
Search within array elements and nested structures
Cross-Application
Search across multiple applications
Date Filtering
Filter results by process creation dates
Prerequisites
Before using the Data Search service, ensure you have:Elasticsearch Configuration
Elasticsearch Configuration
- Elasticsearch cluster running and accessible
- Indexing enabled in FlowX Engine configuration
- Proper network connectivity between services
Kafka Topics
Kafka Topics
KAFKA_TOPIC_DATA_SEARCH_INconfigured for requestsKAFKA_TOPIC_DATA_SEARCH_OUTconfigured for responses- Proper topic permissions and access
Process Data
Process Data
- Process instances with indexed data
- Searchable fields defined in Process Settings → Data Search
- “Update data search” flag enabled on at least one node to trigger indexing
- Completed process instances for reliable results
Quick start
Configure search parameters
Define your search criteria using simple, advanced, or array search syntax.
1. Set up your data process
First, create a process that contains searchable data. Add a Service Task with a business rule: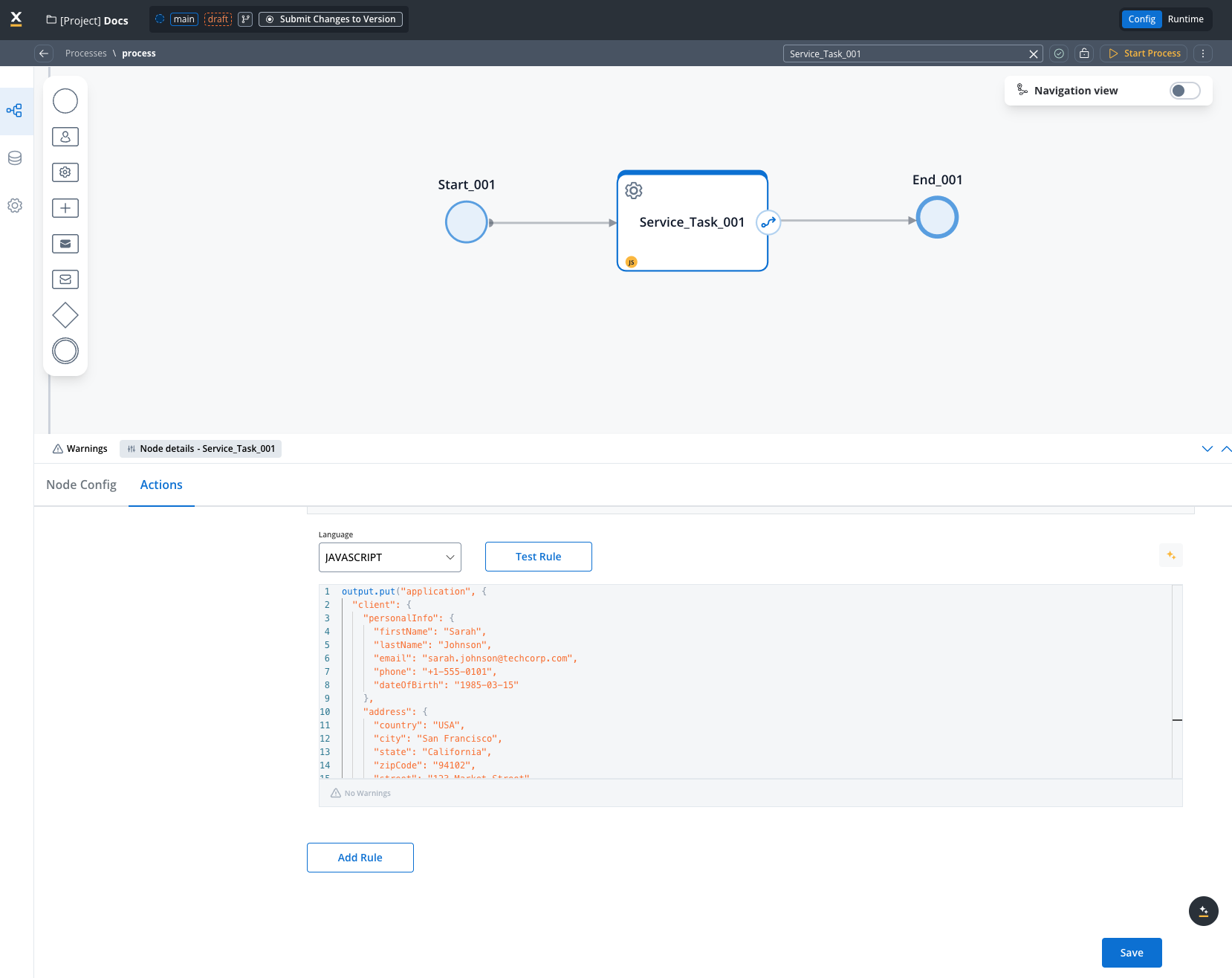
Configure field Indexing
Navigate to Process Settings → Data Search and add the field paths you want to search: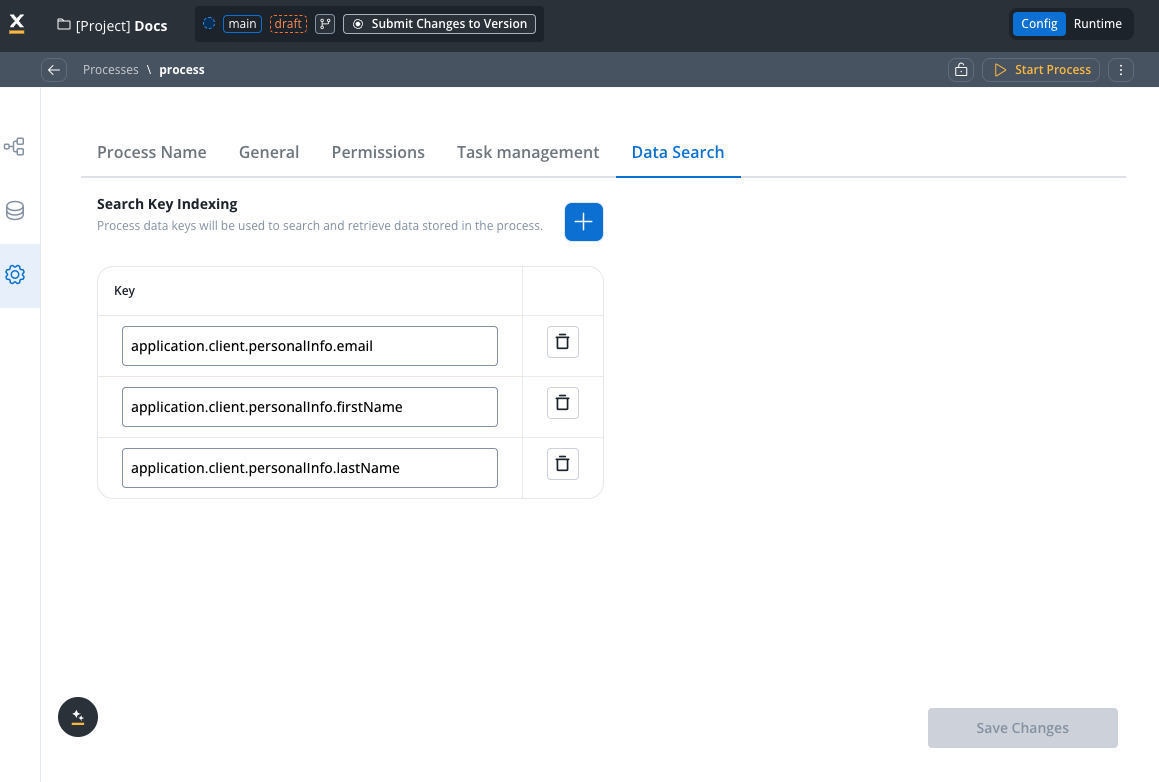
application.client.personalInfo.firstNameapplication.client.personalInfo.lastNameapplication.client.personalInfo.emailapplication.listClient.[].firstName(for array search)application.listClient.[].lastName(for array search)application.listClient.[].department(for array search)
When data gets indexed to Elasticsearch
Data indexing to Elasticsearch occurs only in these specific scenarios:| Trigger | What Gets Indexed |
|---|---|
| Stage changes | All configured indexed fields |
| Swimlane changes | All configured indexed fields |
| ”Update data search” flag enabled on a node | All configured indexed fields |
| Process status changes (STARTED → FINISHED, etc.) | Only the process status, not the data fields |
When a process instance changes status (e.g., from STARTED to FINISHED), only the status itself is updated in Elasticsearch. The actual data fields you configured for indexing are not automatically re-indexed at this point.
Enable the “Update data search” flag
To ensure your data is indexed and searchable, you must enable the Update data search flag on at least one node in your process:- Open a node in your process definition
- Go to Node Config
- Enable the Update data search toggle
- For final data only: Place the flag on the last node before process completion
- For milestone tracking: Place the flag at key checkpoints where you need searchable snapshots
- You don’t need to enable it on every node; only enable it where you need the data to be indexed
2. Create your search process
Create a new process with a Send Message Task: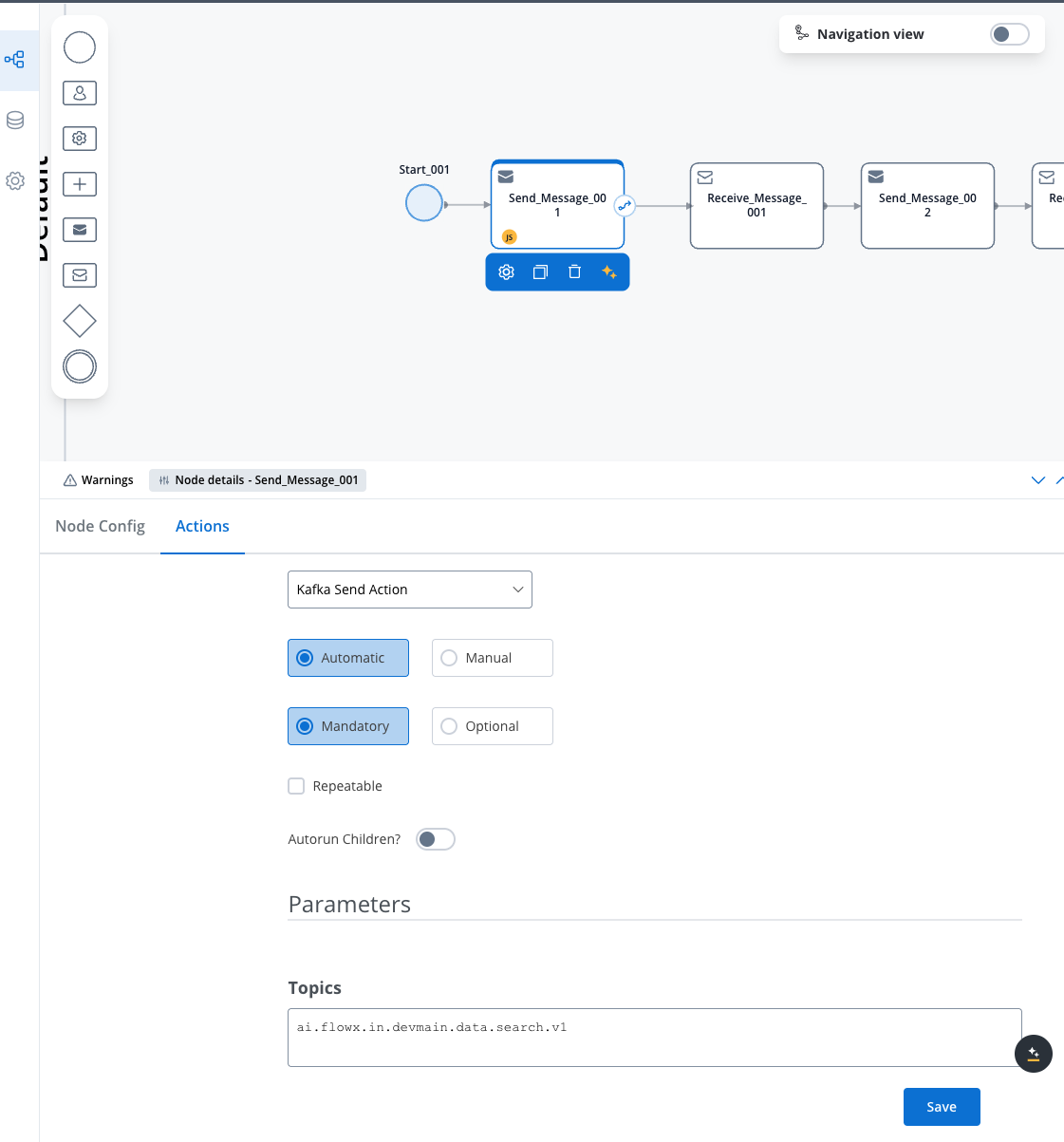
- Action Type: Kafka Send Action
- Topic:
KAFKA_TOPIC_DATA_SEARCH_IN
3. Configure search parameters
Choose your search approach based on your needs:- Simple Search
- Advanced Search
- Array Search
- Cross-Application
- Date Filtering
Use when searching by a single field: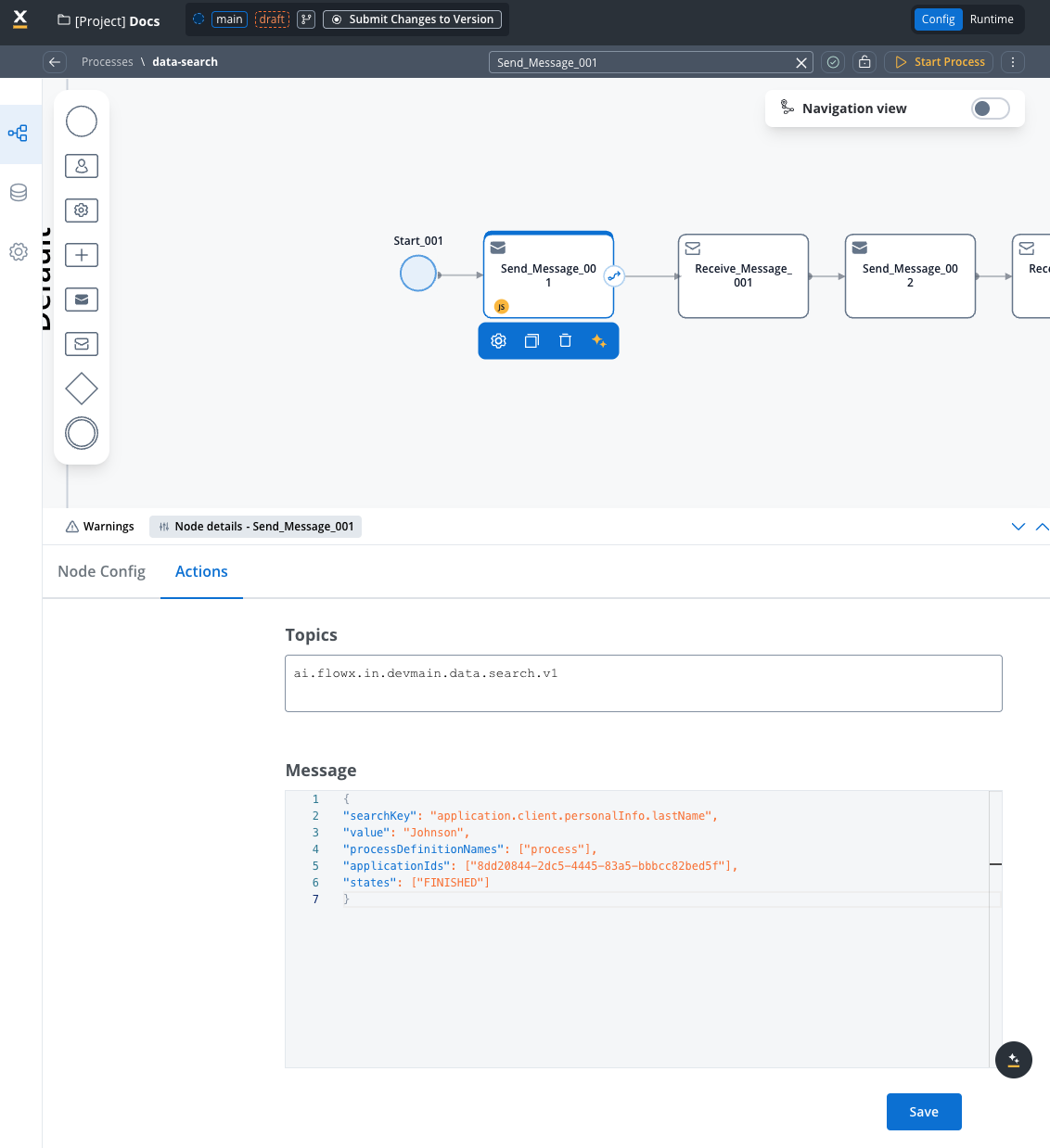

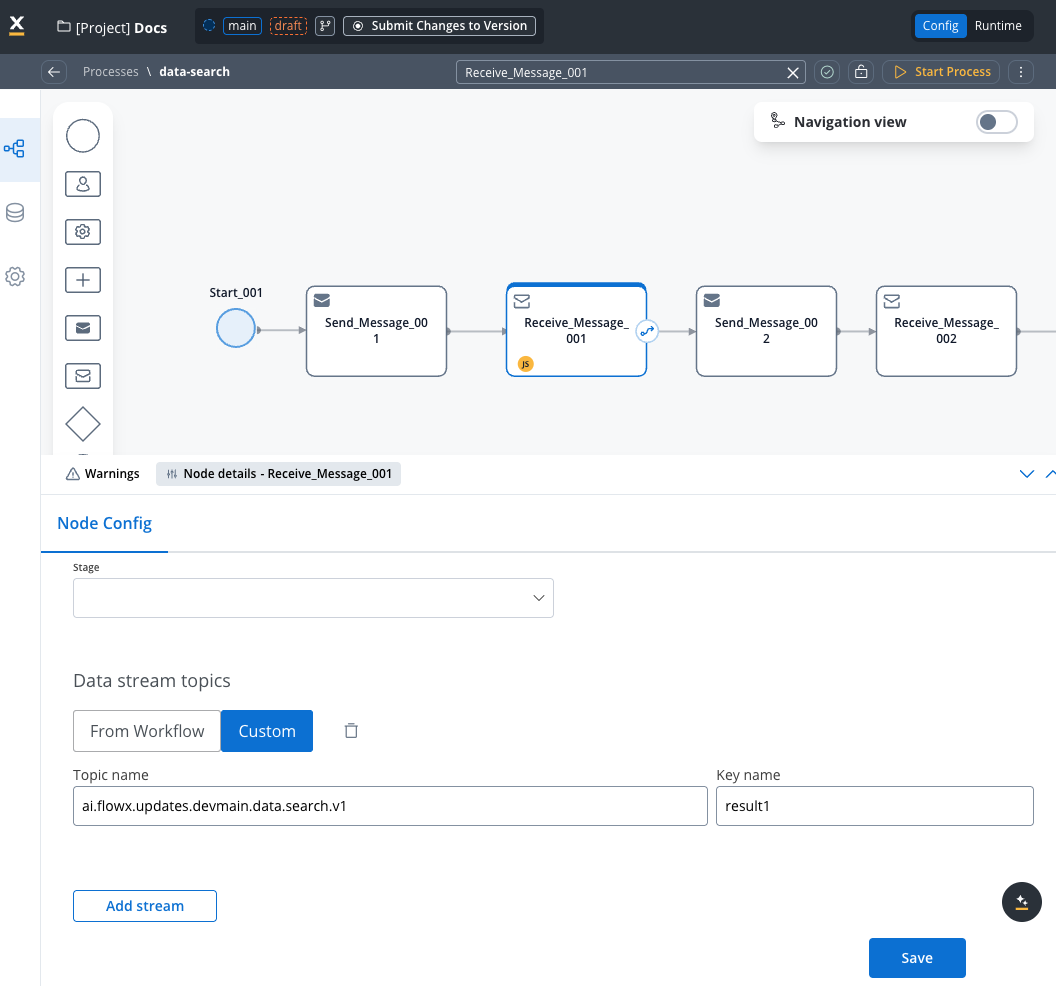
4. Handle search results
Add a Receive Message Task with:- Data Stream:
KAFKA_TOPIC_DATA_SEARCH_OUT
Search parameters reference
Quick reference table
| Parameter | Type | Mandatory | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
searchKey | String | Yes | Single field path to search | "application.client.personalInfo.lastName" |
value | String | Yes | Value to search for (with searchKey) | "Johnson" |
searchKeys | Array | Yes (if multiple fields) | Multiple field-value pairs (AND logic) | [{"key": "field1", "value": "val1"}] |
searchByPaths | Array | Yes (for array search) | Array search field-value pairs | [{"key": "list.[].field", "value": "val"}] |
processDefinitionNames | Array | Yes | Limit to specific processes | ["client_onboarding"] |
applicationIds | Array | No | Search across applications | ["uuid-1", "uuid-2"] |
states | Array | No | Filter by process states | ["FINISHED", "STARTED"] |
processStartDateAfter | String | No | Include processes after date | "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z" |
processStartDateBefore | String | No | Include processes before date | "2024-12-31T23:59:59Z" |
Basic search parameters
searchKey (String)
searchKey (String)
Purpose: The field path to search in for single-field searches.Usage: Use dot notation to specify the exact path to the field you want to search or a specific key in the payload.Examples:
"application.client.personalInfo.firstName""application.client.address.city""application.client.business.industry"
value (String)
value (String)
Purpose: The exact value to search for when using
searchKey.Usage: Must match the stored value exactly (case-sensitive).Examples:"Johnson"- searches for exact lastName match"Technology"- searches for exact industry match"Active"- searches for exact status match
searchKey, not with searchKeys or searchByPaths.searchKeys (Array)
searchKeys (Array)
Purpose: Array of key-value pairs for multi-field searches with AND logic.Usage: All conditions must match for a result to be returned. Can also be used for array searches with Examples:Array Search Example:
[] notation.Format:searchByPaths (Array)
searchByPaths (Array)
Purpose: Array of key-value pairs specifically designed for searching within array elements and nested structures.Usage: Use Examples:Multiple Array Conditions:Nested Array Example:
[] notation to search within array elements. This searches through all items in the array and is the recommended approach for array searches.Format:- Recommended for array searches over
searchKeys - Returns processes where any array element matches the criteria
- Supports deeply nested array structures
Filtering parameters
processDefinitionNames (Array)
processDefinitionNames (Array)
Purpose: Limit search to specific process definitions.Default: Searches all processes if omitted.Usage: Improves performance by narrowing search scope.Examples:
["client_onboarding"]- search only in client processes["employee_registration", "contractor_onboarding"]- search in multiple process types
applicationIds (Array)
applicationIds (Array)
Purpose: Search across specific applications.Default: Searches current application if omitted.Usage: Enable cross-application searches.Examples:
["8dd20844-2dc5-4445-83a5-bbbcc82bed5f"]- search in specific app["app-1-uuid", "app-2-uuid", "app-3-uuid"]- search across multiple apps
states (Array)
states (Array)
Purpose: Filter results by process instance status.Default: Returns all states if omitted.Available States:
"CREATED"- Process instance created but not started"STARTED"- Process is currently running"FINISHED"- Process completed successfully"FAILED"- Process encountered an error and stopped"TERMINATED"- Process was manually stopped/cancelled"ONHOLD"- Process is paused or waiting for external input
["FINISHED"]- only completed processes["STARTED", "ONHOLD"]- active or paused processes["FAILED", "TERMINATED"]- processes that didn’t complete normally
["FINISHED"] for most business searches to get complete data.Date range parameters
processStartDateAfter (String)
processStartDateAfter (String)
Purpose: Include only processes started after the specified date.Format: ISO 8601 timestamp (
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ)Examples:"2024-01-01T00:00:00Z"- processes started after Jan 1, 2024"2024-06-15T09:30:00Z"- processes started after June 15, 2024 at 9:30 AM
- Monthly reports:
"2024-03-01T00:00:00Z" - Recent activity:
"2024-05-20T00:00:00Z"
processStartDateBefore (String)
processStartDateBefore (String)
Purpose: Include only processes started before the specified date.Format: ISO 8601 timestamp (
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ)Examples:"2024-12-31T23:59:59Z"- processes started before end of 2024"2024-06-30T23:59:59Z"- processes started before end of June 2024
- Historical analysis:
"2024-01-01T00:00:00Z" - Quarterly reports:
"2024-03-31T23:59:59Z"
Process states explained
Understanding process states is crucial for effective searching:| State | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| CREATED | Process instance exists but hasn’t started execution | Rarely used for business searches |
| STARTED | Process is actively running | Find ongoing processes, current workload |
| FINISHED | Process completed successfully | Most common for business data searches |
| FAILED | Process encountered an error | Error analysis, troubleshooting |
| TERMINATED | Process was manually cancelled | Audit trails, cancelled applications |
| ONHOLD | Process is paused/waiting | Active cases needing attention |
Recommendation: Use
["FINISHED"] for most business searches to ensure you’re getting complete, reliable data.Response structure
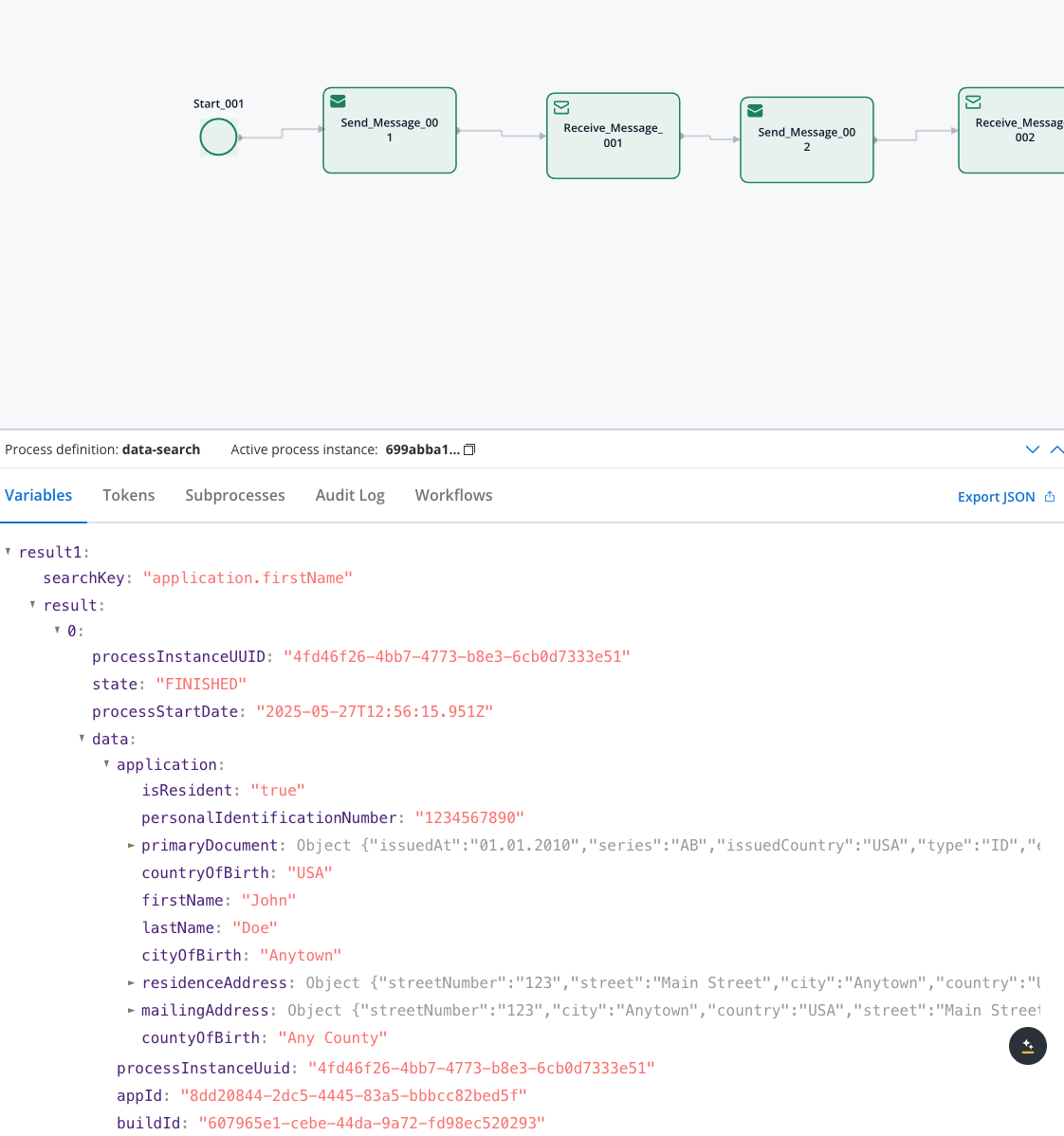
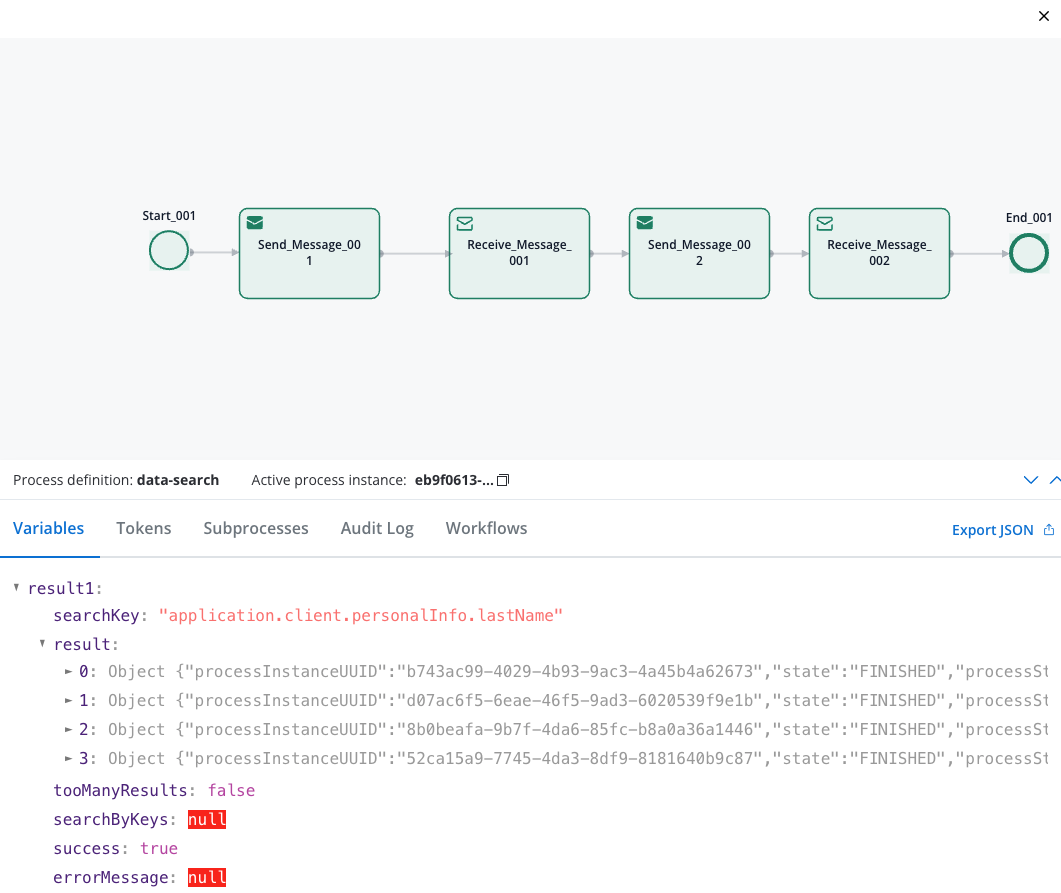
The search returns a JSON object with these fields:result(Array): List of matching process instancesprocessInstanceUUID: Unique process identifierstate: Current process stateprocessStartDate: When the process starteddata: The actual process data with your searchable fields
tooManyResults(Boolean): True if more than 50 results found (limit applied)success(Boolean): Whether the search completed successfullyerrorMessage(String): Error details if search failed
Use cases & examples
HR employee lookup
Search for employees by department, position, or location across HR systems.
Compliance Auditing
Locate specific transactions or approvals for regulatory compliance.
Business Intelligence
Analyze process data patterns and generate reports.
Multi-contact Search
Find processes containing specific individuals within contact lists or arrays.
Real-world example: Employee directory search
HR needs to find employees
HR department needs to find all employees named “Maria” across different departments.
Get comprehensive results
Receive all employee records containing anyone named “Maria” in their employee lists.
Real-world example: Customer support search
Get comprehensive results
Receive full customer profile with account details, order history, and support tickets.
Best practices
Indexing Strategy
Indexing Strategy
- Always enable “Update data search” on at least one node to trigger data indexing
- If you don’t have stages or swimlanes configured, the “Update data search” flag is your only way to index data - without it, your data fields won’t be searchable
- Place the flag strategically: on the last node for final data, or at milestones for intermediate snapshots
- Don’t enable on every node: this creates unnecessary Elasticsearch updates
- Remember: Process status changes (like finishing) only update the status in Elasticsearch, not your data fields
- For long processes, consider enabling at key checkpoints to make data searchable earlier
Array Search Optimization
Array Search Optimization
- Use searchByPaths for array searches instead of searchKeys when possible
- Index array fields properly using
[]notation in Process Settings - Consider array size - large arrays may impact search performance
- Combine array searches with filters to reduce result sets
- Test nested array searches thoroughly before deploying to production
Performance optimization
Performance optimization
- Limit search scope using
processDefinitionNamesandstates - Use date ranges for time-sensitive searches
- Index only frequently searched fields to reduce storage overhead
- Monitor search response times and optimize queries
- Avoid wildcard searches on large datasets
Data Modeling
Data Modeling
- Use consistent field naming across processes
- Normalize data formats (dates, phone numbers, etc.)
- Consider search patterns when designing data structures
- Document indexed fields for team reference
- Plan for data growth and scaling needs
- Design arrays with search in mind - consider what fields will be searched
Security & Compliance
Security & Compliance
- Don’t index sensitive data (SSN, passwords, etc.)
- Implement proper access controls for search endpoints
- Log search activities for audit trails
- Sanitize search inputs to prevent injection attacks
- Follow data retention policies for search results
Error Handling
Error Handling
- Handle empty results gracefully in your UI
- Implement retry logic for failed searches
- Provide meaningful error messages to users
- Set reasonable timeouts for search operations
- Monitor and alert on search failures
Troubleshooting
No Search Results
No Search Results
Possible Causes:
- “Update data search” flag not enabled on any node (most common cause)
- Fields not indexed in Process Settings → Data Search
- Incorrect field path (case-sensitive)
- Process instances not in expected state
- Elasticsearch indexing delay
- Array notation missing for array searches
- Enable “Update data search” on at least one node (typically the last node before completion)
- Verify field indexing configuration in Process Settings → Data Search
- Check exact field paths in process data
- Ensure processes are in FINISHED state
- Wait 30-60 seconds after process completion
- Use
[]notation for array field searches
Data Not Indexed Despite Process Completion
Data Not Indexed Despite Process Completion
Possible Causes:
- “Update data search” flag not enabled on any node
- Misunderstanding of when indexing occurs (status changes only update the status, not data)
- Data added after the last node with the flag enabled
- Enable “Update data search” on the last node before the End Event
- Remember: process status changes (STARTED → FINISHED) only index the status, not your data fields
- Place the “Update data search” flag after all data has been collected
- For milestone-based indexing, enable the flag at each checkpoint where you need searchable data
Array Search Issues
Array Search Issues
Possible Causes:
- Missing
[]notation in field path - Array fields not properly indexed
- Using wrong parameter (
searchKeysvssearchByPaths) - Array is empty or doesn’t contain expected data
- Ensure field path includes
[]for arrays (e.g.,list.[].field) - Verify array fields are indexed with
[]notation - Use
searchByPathsfor array searches when possible - Check that arrays contain the expected data structure
- Test with simple array structures first
Search Timeout Errors
Search Timeout Errors
Possible Causes:
- Query too broad (searching all data)
- Elasticsearch cluster performance issues
- Large dataset without proper filtering
- Complex nested array searches
- Add more specific filters (
processDefinitionNames,states) - Use date ranges to limit scope
- Check Elasticsearch cluster health
- Optimize indexing strategy
- Simplify complex array search patterns
Invalid Search Key Errors
Invalid Search Key Errors
Possible Causes:
- Typos in field paths
- Field doesn’t exist in process data
- Incorrect JSON format in request
- Missing array notation for array fields
- Verify field paths exist in process instances
- Check for case sensitivity
- Validate JSON syntax
- Test with simple field paths first
- Add
[]notation for array field searches
Connection Issues
Connection Issues
Possible Causes:
- Kafka topics not properly configured
- Network connectivity problems
- Service authentication issues
- Verify Kafka topic configuration
- Check network connectivity
- Validate service credentials
- Review FlowX Engine logs

