React project requirements
Your app MUST use SCSS for styling.
To install the npm libraries provided by FlowX.AI you will need to obtain access to the private FlowX.AI Nexus registry. Please consult with your project DevOps.
The library uses React version react~18, npm v10.8.0 and node v18.16.9.
Installing the library
Use the following command to install the renderer library and its required dependencies:
Installing react and react-dom can be skipped if you already have them installed in your project.
npm install \
react@18 \
react-dom@18 \
@flowx/core-sdk@<version> \
@flowx/core-theme@<version> \
@flowx/react-sdk@<version> \
@flowx/react-theme@<version> \
@flowx/react-ui-toolkit@<version> \
air-datepicker@3 \
axios \
ag-grid-react@32
Replace <version> with the correct version corresponding to your platform version.To find the right version, navigate to: Release Notes → Choose your platform version → Deployment guidelines → Component versions.
Initial setup
Once installed, FlxProcessRenderer will be imported in the from the @flowx/react-sdk package.
Theming
Component theming is done through the @flowx/react-theme library. The theme id is a required input for the renderer SDK component and is used to fetch the theme configuration. The id can be obtained from the admin panel in the themes section.
Authorization
It’s the responsibility of the client app to implement the authorization flow (using the OpenID Connect standard). The renderer SDK will expect the authToken to be passed to the FlxProcessRenderer as an input.
import { FlxProcessRenderer } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
export function MyFlxContainer() {
return <FlxProcessRenderer
apiUrl={'your API url'}
language={...}
authToken={...}
processName={...}
processStartData={...}
workspaceId={...}
processApiPath={...}
themeId="12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012"
staticAssetsPath={...}
locale="en-US"
language="en"
projectInfo={
projectId: ...
}
/>
}
FlxProcessRenderer component is required in the application module where the process will be rendered. The component accepts a props where you can pass extra config info, register a custom component or custom validators.
Custom components will be referenced by name when creating the template config for a user task.
Custom validators will be referenced by name (customValidator) in the template config panel in the validators section of each generated form field.
import { FlxProcessRenderer } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
export function MyFlxContainer() {
return <FlxProcessRenderer
apiUrl={'your API url'}
language={...}
authToken={...}
processName={...}
processStartData={...}
workspaceId={...}
processApiPath={...}
themeId="12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012"
components={{ MyCustomComponentIdentifier: MyCustomComponent }}
validators={{ customValidator: (...params: string[]) => (v: string) => v === '4.5'}}
staticAssetsPath={...}
locale="en-US"
language="en"
projectInfo={{
projectId: ...
}}
/>
}
<FlxProcessRenderer /> component. A list of accepted inputs is found below:
<FlxProcessRenderer
apiUrl={apiUrl}
language={language}
authToken={authToken}
processName={processName}
processStartData={processStartData}
workspaceId={workspaceId}
processApiPath={apiPath}
themeId={themeId}
components={customComponents}
validators={validators}
staticAssetsPath={assetsPath}
locale={locale}
language={language}
projectInfo={projectInfo}
/>
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Default value | Example |
|---|
| apiUrl | Your base url | string | true | - | https://yourDomain.dev |
| processApiPath | Process subpath | string | true | - | onboarding |
| authToken | Authorization token | string | true | - | ‘eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIn…‘ |
| themeId | Theme id used to style the process. Can be obtained from the themes section in the admin | string | true | - | ‘123-456-789’ |
| processName | Identifies a process | string | true | - | client_identification |
| processStartData | Data required to start the process | json | true | - | { "firstName": "John", "lastName": "Smith"} |
| workspaceId | Workspace id | string | true | - | ‘8f52744-8403-4e8d…‘ |
| language | Language used to localize the enumerations inside the application. | string | false | ro | - |
| isDraft | When true allows starting a process in draft state. *Note that isDraft = true requires that processName be the id (number) of the process and NOT the name. | boolean | false | false | - |
| locale | Defines the locale of the process, used to apply date, currency and number formatting to data model values | boolean | false | ro-RO | - |
| projectInfo | Defines which FlowX Project will be run inside the process renderer. | json | true | - | { "projectId": "111111-222222-333333-44444"} |
| customLoader | Custom loader components for different loading scenarios. | object | false | - | { startProcess: <LoaderComponent />, saveData: <ActionLoader /> } |
Analytics
The SDK provides a mechanism for collecting analytics events through a unified CustomEvent system. These events can be used to track screens and action events.
import {
ANALYTICS_EVENTS,
AnalyticsData,
pushAnalyticsData,
} from '@flowx/core-sdk';
Emitting Analytics Events
Analytics events are dispatched using the pushAnalyticsData(payload: AnalyticsData) method. The SDK defines two event types:
enum ANALYTICS_EVENTS {
SCREEN = 'SCREEN',
ACTION = 'ACTION',
}
type AnalyticsData = {
type: ANALYTICS_EVENTS;
value: string;
screen?: string;
component?: string;
label?: string;
customPayload?: object;
}
The value property represents the identifier set in the process definition.For ACTION type events there are some additional properties provided:
- component - The type of component triggering the action
- label - The label of the component
- screen - The identifier of the screen containing the component, if set
Listening for Analytics Events
You can subscribe to analytics events using the standard CustomEvent API:
const analyticsListener = (event: CustomEvent<AnalyticsData>) => {
console.log('Received flowx:analytics event:', event.detail);
}
useEffect(() => {
document.addEventListener('flowx:analytics', analyticsListener)
return () => {
document.removeEventListener('flowx:analytics', analyticsListener)
}
}, [])
Ensure that you remove the event listener on component destruction to avoid memory leaks.
Custom Payload
This functionality, allowing you to capture and send custom data alongside standard analytics events.
When analytics custom payload is configured in FlowX Designer, the renderer automatically processes variable substitution and includes the resulting data in analytics events.
Receive custom payload configuration
The renderer receives the analytics configuration as a JSON string with variable placeholders:"analyticsCustomPayload": "{\n \"name\": ${app.input}\n}"
Process variable substitution
The SDK replaces variables with actual values from the process data store:{
"name": "${app.input}",
"client": "${app.client}",
"amount": "${app.amount}"
}
Add to analytics event
The processed payload is included in the analytics event under the customPayload property:// Analytics event structure with custom payload
{
type: 'ACTION', // or 'SCREEN'
info: {
value: 'Save personal data',
screen: 'Personal Data',
component: 'BUTTON',
label: 'Save',
customPayload: {
name: "john",
client: { id: "123", name: "John Doe" },
amount: 1500
}
}
}
Starting a process
Prerequisites
-
Process Name: You need to know the name of the process you want to start. This name is used to identify the process in the system.
-
FlowX Project UUID: You need the UUID of the FlowX Project that contains the process you want to start. This UUID is used to identify the project in the system.
-
Locale: You can specify the locale of the process to apply date, currency, and number formatting to data model values.
-
Language: You can specify the language used to localize the enumerations inside the application.
Getting the project UUID
The project UUID can be obtained from the FlowX Dashboard. Navigate to the Projects section and select the project you want to start a process in. The UUID can be copied from the project actions popover.
Getting the process name
The process name can be obtained from the FlowX Designer. Navigate to the process you want to start and copy the process name from the breadcrumbs.
Initializing the process renderer
To start a process, you need to initialize the FlxProcessRenderer component in your application. The component accepts various props that define the process to start, the theme to use, and other configuration options.
import { FlxProcessRenderer } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
export function MyFlxContainer() {
return <FlxProcessRenderer
{...props}
locale="en-US"
language="en"
processName={processName}
projectInfo={{ projectId }}
/>
}
Custom components
Custom components will be hydrated with data through the data input prop which must be defined in the custom component.
Custom components will be provided through the components parameter to the <FlxProcessRenderer /> component.
The object keys passed in the components prop MUST match the custom component names defined in the FlowX process.
Component data defined through an inputKey is available under data -> data
Component actions are always found under data -> actionsFn key.
export const MyCustomComponent = ( {data }) => {...}
# data object example
data: {
data: {
input1: ''
},
actionsFn: {
action_one: () => void;
action_two: () => void; }
}
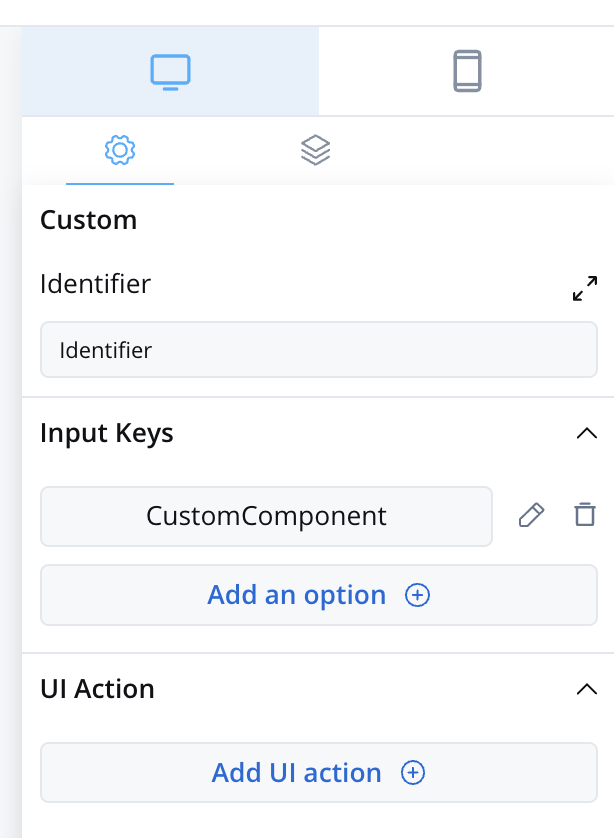
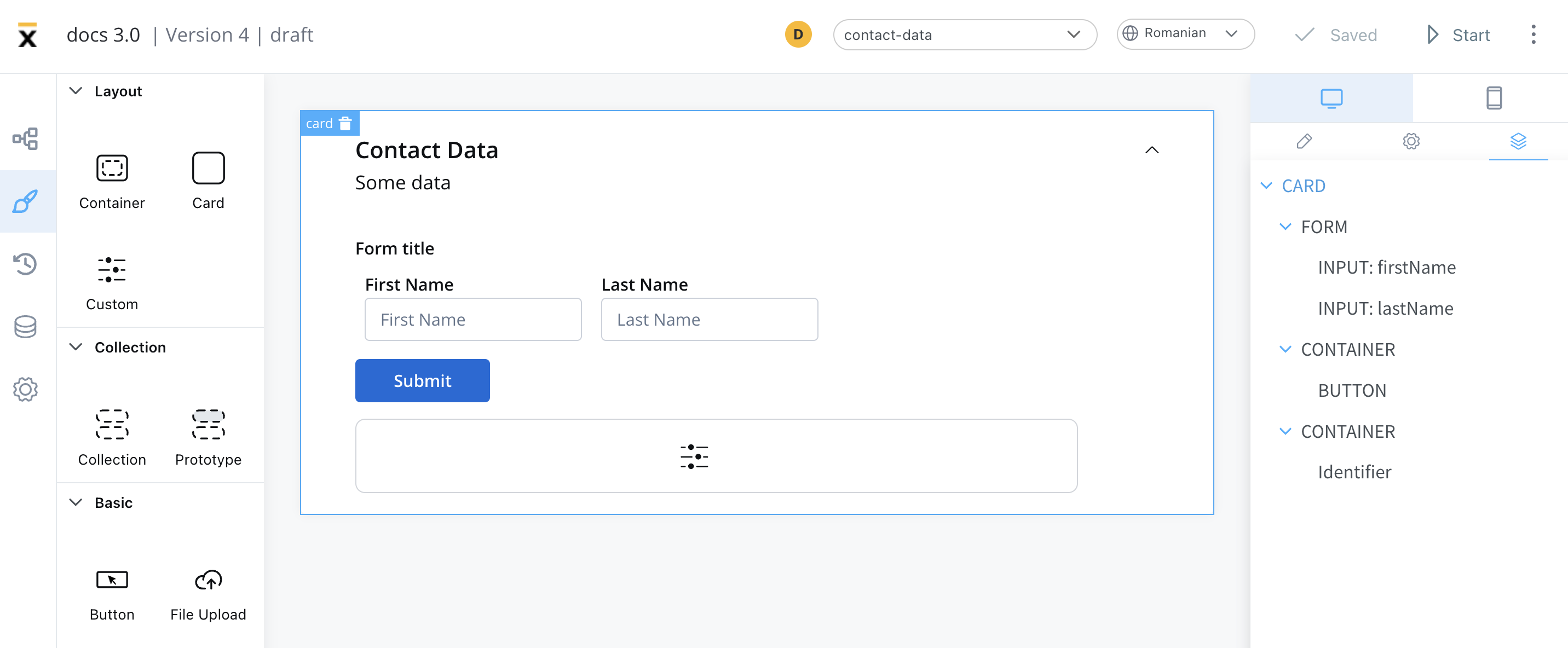 The properties that can be configured are as follows:
The properties that can be configured are as follows:
- Identifier - This enables the custom component to be displayed within the component hierarchy and determines the actions available for the component.
- Input keys - These are used to specify the pathway to the process data that components will utilize to receive their information.
- UI Actions - actions defined here will be made available to the custom component
Prerequisites (before creation)
-
React Knowledge: You should have a good understanding of React, as custom components are created and imported using React.
-
Development Environment: Set up a development environment for React development, including Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager).
-
Component Identifier: You need a unique identifier for your custom component. This identifier is used for referencing the component within the application.
Creating a custom component
To create a Custom Component in React, follow these steps:
- Create a new React component.
- Implement the necessary HTML structure, TypeScript logic, and SCSS styling to define the appearance and behavior of your custom component.
Importing the component
After creating the Custom Component, you need to import it into your application.
In your <FlxProcessRenderer /> component, add the following property:
<FlxProcessRenderer
{...otherProps}
components={{ MyCustomComponentIdentifier: MyCustomComponent }}
/>
Using the custom component
Once your Custom Component is declared, you can use it for configuration within your application.
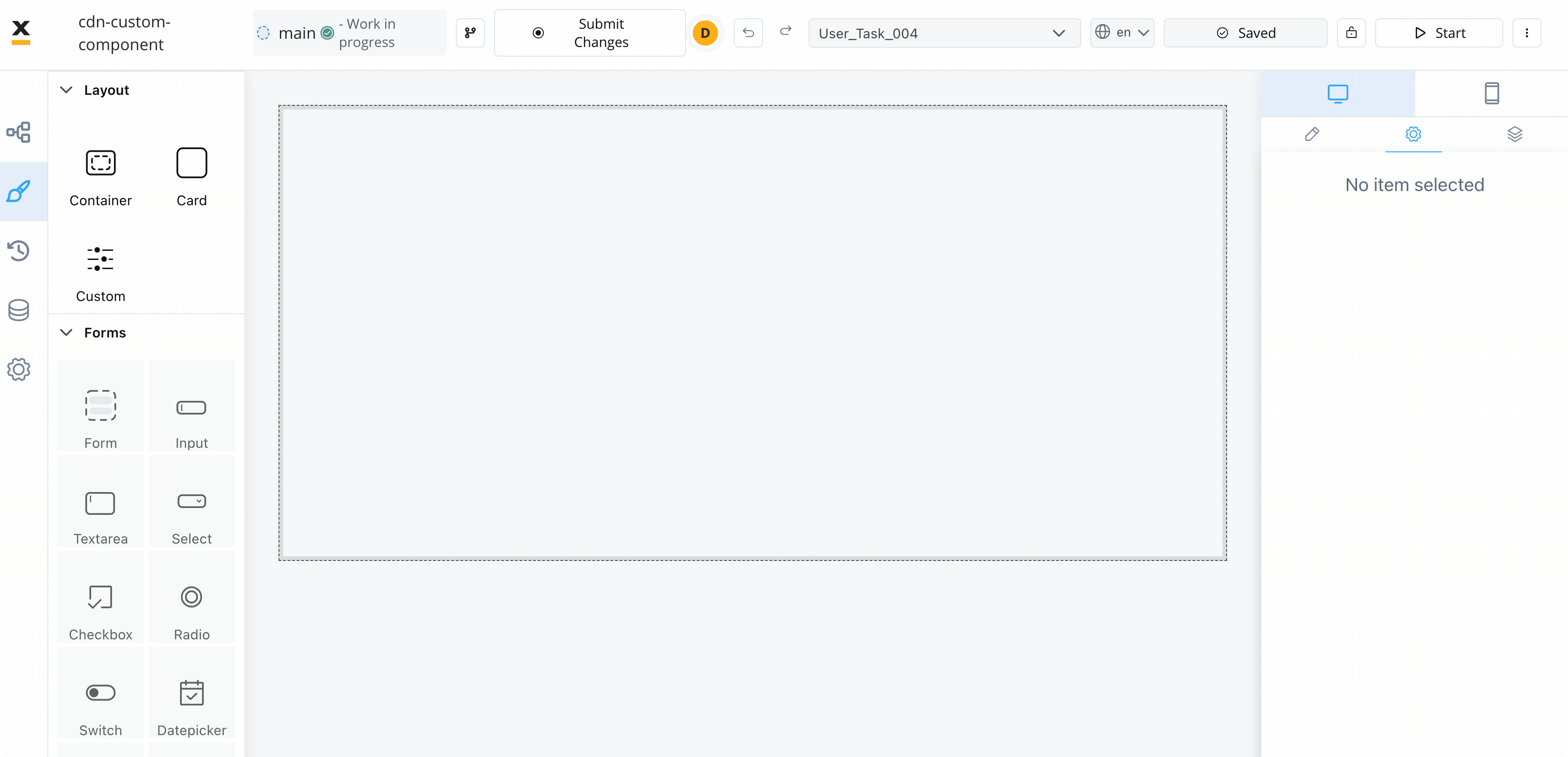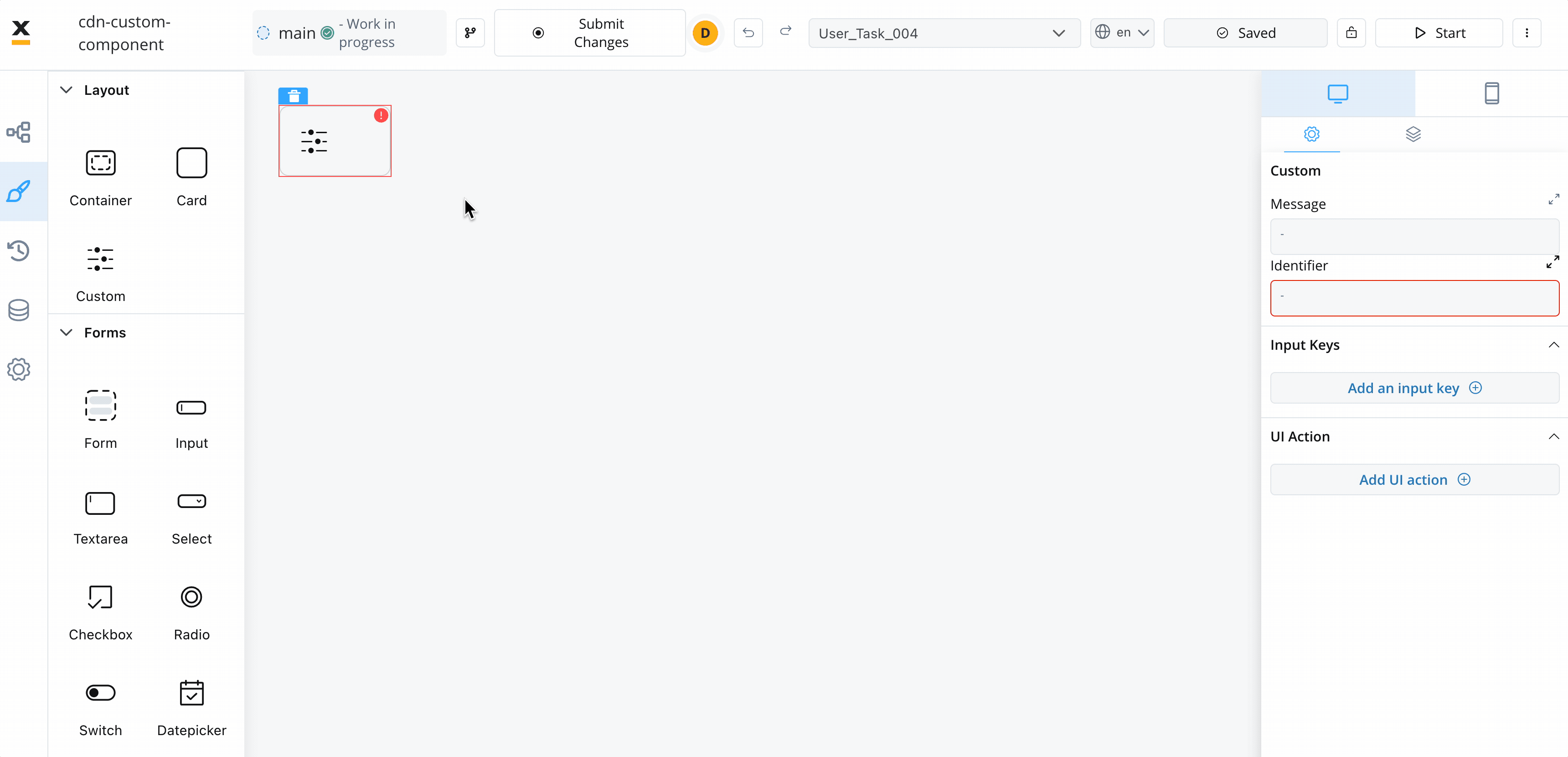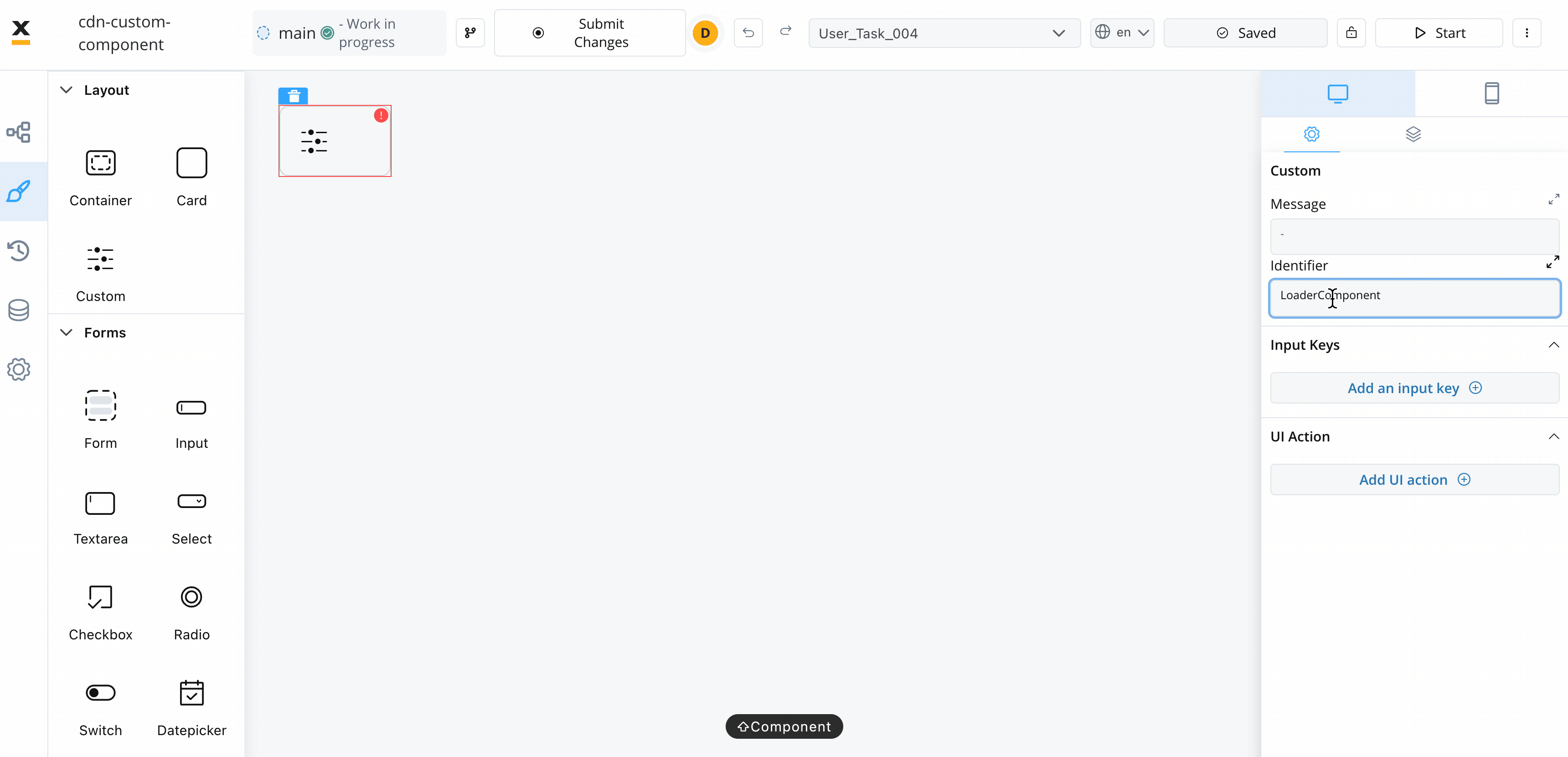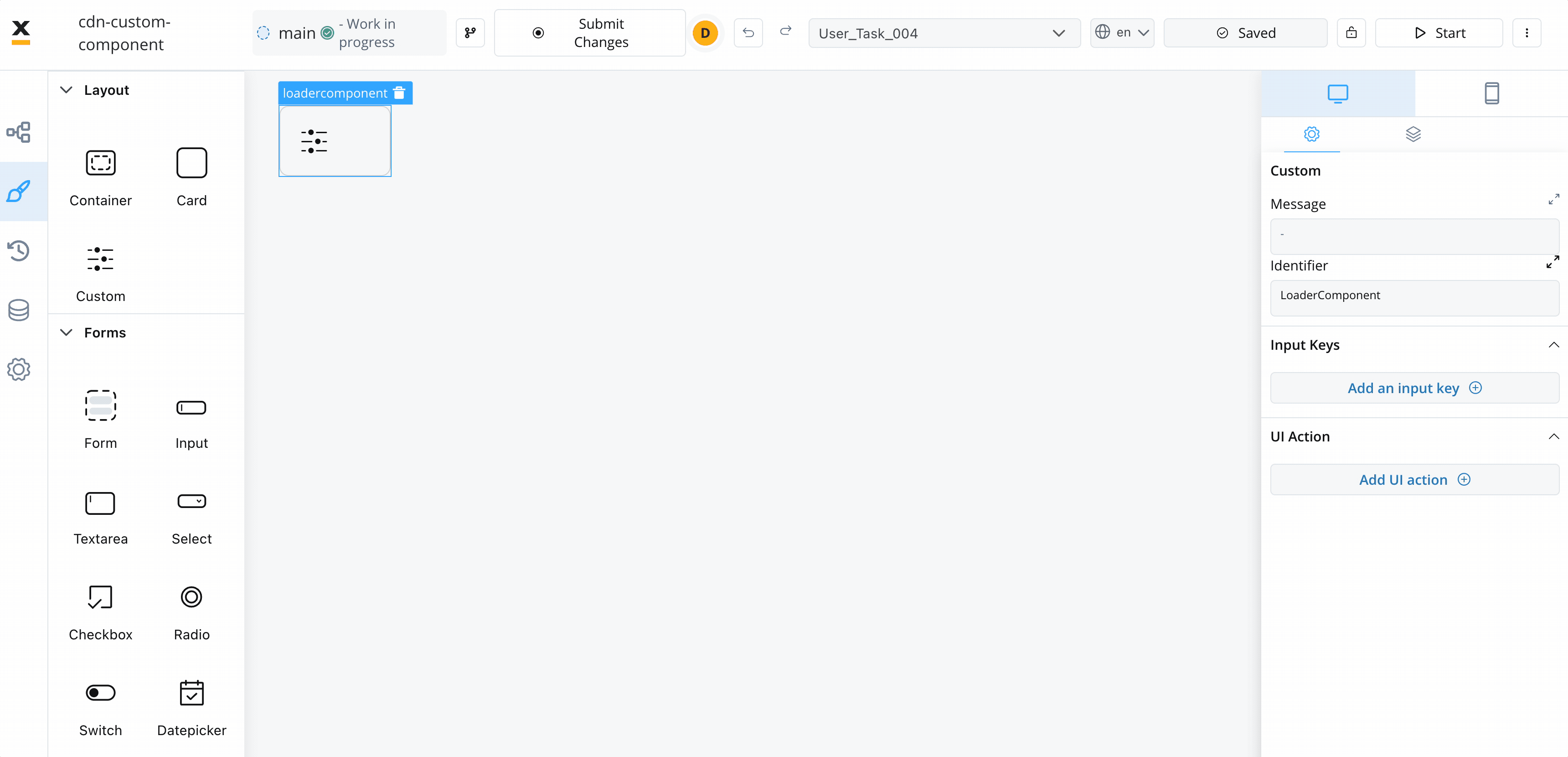 The Custom Component accepts input data from processes and can also include actions extracted from a process. These inputs and actions allow you to configure and interact with the component dynamically.
The Custom Component accepts input data from processes and can also include actions extracted from a process. These inputs and actions allow you to configure and interact with the component dynamically.
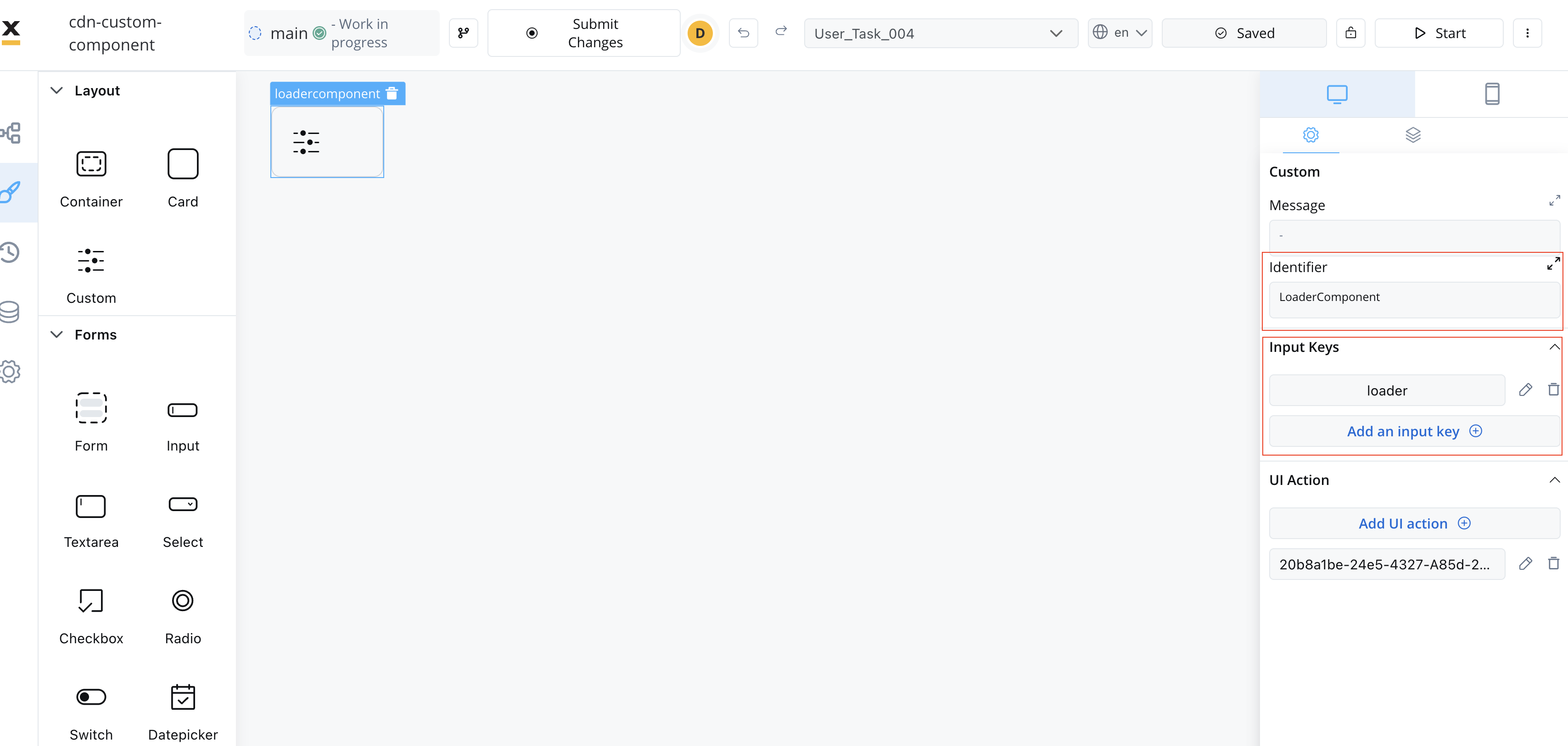 There are multiple ways to extract data from processes to use within your Custom Component. You can utilize the data provided by the process or map actions from the BPMN process to Angular actions within your component.
There are multiple ways to extract data from processes to use within your Custom Component. You can utilize the data provided by the process or map actions from the BPMN process to Angular actions within your component.
Make sure that the React actions that you declare match the names of the process actions.
Styling with CSS
To apply CSS classes to UI elements within your Custom Component, you first need to identify the UI element identifiers within your component’s HTML structure. Once identified, you can apply defined CSS classes to style these elements as desired.
Example:
Additional considerations
-
Naming Conventions: Be consistent with naming conventions for components, identifiers, and actions. Ensure that Angular actions match the names of process actions as mentioned in the documentation.
-
Component Hierarchy: Understand how the component fits into the overall component hierarchy of your application. This will help determine where the component is displayed and what actions are available for it.
-
Documentation and Testing: Document your custom component thoroughly for future reference. Additionally, testing is crucial to ensure that the component behaves as expected in various scenarios.
-
Security: If your custom component interacts with sensitive data or performs critical actions, consider security measures to protect the application from potential vulnerabilities.
-
Integration with FLOWX Designer: Ensure that your custom component integrates seamlessly with FLOWX Designer, as it is part of the application’s process modeling capabilities.
Custom validators
You may also define custom validators in your FlowX processes and pass their implementation through the validators prop of the <FlxProcessRenderer /> component.
The validators are then processed and piped through the popular React Hook Form library, taking into account how the error messages are defined in your process.
A validator must have the following type:
const customValidator = (...params: string[]) => (v: any) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
The object keys passed in the validators prop MUST match the custom validator names defined in the FlowX process.
Process end handling
The SDK provides a mechanism for container applications to handle process completion events through the onProcessEnded callback. This allows you to implement custom logic when a main process reaches an end state, such as redirecting users or triggering cleanup operations.
The onProcessEnded callback is triggered when the main process (not subprocesses) reaches any terminal state:
FINISHED - Process completed successfullyFAILED - Process encountered an errorABORTED - Process was manually terminated- Other terminal states
Only the main process triggers this callback. Subprocess completions do not trigger the callback to avoid unnecessary interruptions during complex process flows.
Implementation
To handle process end events, pass a function to the onProcessEnded prop of the <FlxProcessRenderer /> component:
import { FlxProcessRenderer } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
export function MyFlxContainer() {
const handleProcessEnd = () => {
// Your custom logic here
console.log('Process has ended');
// Example: Redirect to home page
window.location.href = '/dashboard';
};
return (
<FlxProcessRenderer
{...otherProps}
onProcessEnded={handleProcessEnd}
/>
);
}
Custom loader
The SDK provides a mechanism for container applications to customize the loader UI displayed during process execution. This allows you to replace the default FlowX loader with your own custom implementation based on different loading scenarios.
Configuration
To configure custom loaders, pass them through the customLoader prop of the <FlxProcessRenderer /> component:
import { FlxProcessRenderer } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
// Define your custom loader components
const StartProcessLoader = () => (
<div className="custom-start-loader">
<div className="spinner" />
<p>Starting process...</p>
</div>
);
const SpecificActionLoader = () => (
<div className="custom-specific-action-loader">
<div className="spinner" />
<p>Executing specific action...</p>
</div>
);
// Register the custom loaders in your component
export function MyFlxContainer() {
return (
<FlxProcessRenderer
{...otherProps}
customLoader={{
startProcess: <StartProcessLoader />,
// reloadProcess: <ReloadProcessLoader />,
// defaultAction: <DefaultActionLoader />,
// defaultUpload: <DefaultUploadLoader />,
actions: {
action1: <SpecificActionLoader />,
// action2: <SaveDataLoader />,
},
}}
/>
);
}
API Specification
The customLoader prop accepts an object of type CustomLoader:
type CustomLoader = {
actions?: Record<string, ReactNode>
startProcess?: ReactNode
reloadProcess?: ReactNode
defaultAction?: ReactNode
defaultUpload?: ReactNode
}
Loader Types
startProcess - Displayed when starting or resuming a processreloadProcess - Displayed when reloading a processdefaultAction - Default loader for actions when loaderType is 'action'. Used when no specific action loader is found in the actions recorddefaultUpload - Default loader for file uploads when loaderType is 'upload'actions - Record mapping specific action identifiers to custom loaders. When an action is executed, the SDK will first check for a matching entry in this record before falling back to defaultAction
Fallback Behavior
If no custom loader is provided for a specific type, the SDK will automatically fall back to the built-in FlowX loader. This ensures your application continues to function even with partial custom loader configuration.
You can use any React components, including those with animations, styled components, or media assets, to create rich loading experiences that match your application’s design system.
Chat component
To use the FlxChatRenderer component, import the module in your project:
import { FlxChatRenderer } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
Usage
Include the component in your template:
<FlxChatRenderer
apiUrl={baseUrl}
authToken={accessToken}
staticAssetsPath={staticAssetsPath}
language={language}
locale={locale}
themeId={themeId}
projectId={projectId}
workspaceId={workspaceId}
source={source}
chatConfig={chatConfig}
cache={cache}
/>
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
apiUrl | Your base API URL | string | ✅ | https://yourDomain.dev |
authToken | Authorization token | string | ✅ | (retrieved from auth provider) |
staticAssetsPath | Path for static resources | string | ❌ | (set via environment) |
language | Language used to localize the chat interface | string | ❌ | en |
locale | Locale setting for date and number formatting | string | ❌ | en-US |
themeId | Theme identifier for styling | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
projectId | The FlowX project ID | string | ✅ | (retrieved dynamically) |
workspaceId | The workspace ID | string | ✅ | (retrieved dynamically) |
source | Source object with type and id | object | ✅ | { type: 'WORKFLOW', id: '...' } |
chatConfig | Chat configuration object | object | ❌ | { welcomeMessage: '...', ... } |
cache | Enable caching for chat responses | boolean | ❌ | true |
chatConfig parameters
The chatConfig object accepts the following properties:
| Name | Description | Type | Default value |
|---|
welcomeMessage | Message displayed when chat is first opened | string | 'Welcome to the chat!' |
thinkingMessage | Message displayed while waiting for response | string | 'Thinking...' |
title | Chat window title | string | 'Chat' |
subtitle | Chat window subtitle | string | 'Chat subtitle' |
showChatIcon | Whether to display the chat icon | boolean | true |
showSeparator | Whether to show separator between messages | boolean | true |
newChatLabel | Label for the new chat button | string | 'New chat' |
inputPlaceholder | Placeholder text for the message input field | string | 'Enter your message' |
maxInputRows | Maximum number of rows for the input field | number | 10 |
Task management component
To use the FlxTaskManager component, import the module in your project:
import { FlxTaskManager } from '@flowx/react-sdk';
Usage
Include the component in your template:
<FlxTaskManager
apiUrl={baseUrl}
authToken={authToken}
appInfo={appInfo}
viewId={viewId}
workspaceId={workspaceId}
themeId={themeId}
language={language}
locale={locale}
staticAssetsPath={staticAssetsPath}
buildId={buildId}
/>
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
apiUrl | Endpoint where the tasks are available | string | ✅ | https://yourDomain.dev/tasks |
authToken | Authorization token | string | ✅ | (retrieved from local storage) |
appInfo | Application information object containing appId | object | ✅ | { appId: "app-123" } |
viewId | The view configuration identifier | string | ✅ | (retrieved dynamically) |
workspaceId | The workspace ID | string | ✅ | (retrieved dynamically) |
themeId | The theme identifier | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
language | The selected language | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
locale | The localization setting | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
buildId | The current build identifier | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
staticAssetsPath | Path for static resources | string | ❌ | (set via environment) |
Task management public API
The React SDK provides a comprehensive public API for building custom task management interfaces.
This API allows you to fetch tasks, manage comments, handle task actions, and interact with task data programmatically.
Importing the API
To use the task management public API, import the functions and types from @flowx/react-sdk:
import {
// Functions
getTaskManagerResources,
fetchView,
fetchViewTasks,
fetchTaskComments,
fetchTaskHistory,
fetchTaskAssignees,
updateTaskAction,
saveComment,
removeComment,
updateTaskPriority,
updateBulkTaskAction,
fetchBulkAssignees,
getEnumerationOptions,
initSseConnection,
// Types and Interfaces
TaskManagerSetupOptions,
View,
ViewTask,
ViewColumn,
ViewFilter,
TaskActions,
TaskComment,
TaskHistory,
Assignees,
TaskManagerEnumeration,
SseConnection,
SseEventData,
SseMessageType,
SseTaskMessageType,
} from '@flowx/react-sdk'
Initialization
Before using the task management API, you need to initialize the task manager resources. This fetches the view configuration, enumerations, and filter operators.
const { view, enumerations, filterOperators } = await getTaskManagerResources({
apiUrl: 'https://yourDomain.dev/tasks',
authToken: 'your-auth-token',
appInfo: { appId: 'app-123' },
viewId: 'view-456',
workspaceId: 'workspace-789',
themeId: 'theme-012', // Optional
language: 'en', // Optional
locale: 'en-US', // Optional
buildId: 'build-345', // Optional
staticAssetsPath: '/static', // Optional
})
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
apiUrl | Endpoint where the tasks are available | string | ✅ | https://yourDomain.dev/tasks |
authToken | Authorization token | string | ✅ | (retrieved from local storage) |
appInfo | Application information object containing appId | { appId: string } | ✅ | { appId: "app-123" } |
viewId | The view configuration identifier | string | ✅ | (retrieved dynamically) |
workspaceId | The workspace ID | string | ✅ | (retrieved dynamically) |
themeId | The theme identifier | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
language | The selected language | string | ❌ | "en" |
locale | The localization setting | string | ❌ | "en-US" |
buildId | The current build identifier | string | ❌ | (retrieved dynamically) |
staticAssetsPath | Path for static resources | string | ❌ | (set via environment) |
view: The view configuration objectenumerations: Available enumeration options for filtersfilterOperators: Available filter operators for each column
Fetching Tasks
fetchViewTasks
Fetches tasks for a specific view with support for sorting, filtering, pagination, and search.
const response = await fetchViewTasks(
sort, // Array of sort configurations
filters, // Array of filter configurations
searchTerm, // Search string
view, // View object from getTaskManagerResources
pagination, // Pagination object { page: number, size: number }
enumerations // Enumerations from getTaskManagerResources
)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
sort | Array of sort configurations | ViewTasksSort[] | ✅ | [{ keyName: "priority", direction: "ASC" }] |
filters | Array of filter configurations | ViewTasksFilter[] | ✅ | See filter examples below |
searchTerm | Search string for task search | string | ✅ | "urgent" |
view | View object from initialization | View | ✅ | (from getTaskManagerResources) |
pagination | Pagination configuration | { page: number, size: number } | ✅ | { page: 0, size: 10 } |
enumerations | Enumerations from initialization | TaskManagerEnumerations | ✅ | (from getTaskManagerResources) |
content: Array of ViewTask objectstotalElements: Total number of taskstotalPages: Total number of pages- Other pagination metadata
Example:
const sort = [{ keyName: 'priority', direction: 'ASC' }]
const filters = [
{
keyName: 'status',
operator: 'EQUALS',
value: ['PENDING'],
keyType: 'enumType',
columnType: 'status',
},
]
const pagination = { page: 0, size: 10 }
const response = await fetchViewTasks(
sort,
filters,
'', // searchTerm
view,
pagination,
enumerations
)
const tasks = response.content // Array of ViewTask objects
fetchView
Fetches a specific view configuration by ID.
const view = await fetchView(viewId)
Task Details
Fetches all comments for a specific task.
const comments = await fetchTaskComments(taskId)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
TaskComment objects.
Example:
const comments = await fetchTaskComments(selectedTask.id)
// Returns: [
// {
// commentId: "comment-1",
// message: "This task needs attention",
// author: { username: "john.doe", ... },
// createdAt: "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"
// }
// ]
fetchTaskHistory
Fetches the history/audit trail for a specific task.
const history = await fetchTaskHistory(taskId)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
TaskHistory objects.
Example:
const history = await fetchTaskHistory(selectedTask.id)
// Returns: [
// {
// historyId: "history-1",
// events: [
// {
// type: "STATUS_CHANGED",
// description: "Status changed from PENDING to IN_PROGRESS"
// }
// ]
// }
// ]
fetchTaskAssignees
Fetches available assignees for a task, with optional search filtering.
const assignees = await fetchTaskAssignees(
taskId,
tokenUuid,
options
)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
tokenUuid | The token UUID associated with task | string | ✅ | "token-uuid-456" |
options | Search options | object | ❌ | { keyword: "john" } |
Assignees objects.
Example:
const users = await fetchTaskAssignees(
selectedTask.id,
selectedTask.tokenUuid,
{ keyword: 'john' }
)
// Returns: [
// {
// username: "john.doe",
// firstName: "John",
// lastName: "Doe",
// email: "john.doe@example.com"
// }
// ]
fetchBulkAssignees
Fetches available assignees for multiple tasks in bulk.
const assignees = await fetchBulkAssignees(
taskIds,
options
)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskIds | Array of task IDs | string[] | ✅ | ["task-1", "task-2"] |
options | Search options | object | ❌ | { keyword: "john" } |
Assignees objects.
Task Actions
updateTaskAction
Executes an action on a specific task (e.g., assign, complete, cancel).
await updateTaskAction(
action,
taskId,
tokenUuid,
username
)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
action | The action to execute | ExecuteTaskActions | ✅ | TaskActions.ASSIGN |
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
tokenUuid | The token UUID associated with task | string | ✅ | "token-uuid-456" |
username | Username for assign action (optional) | string | ❌ | "john.doe" |
TaskActions.ASSIGN - Assign task to a userTaskActions.COMPLETE - Mark task as completeTaskActions.CANCEL - Cancel the taskTaskActions.CHANGE_PRIORITY - Change task priorityTaskActions.VIEW - View task details
Example:
// Assign task to a user
await updateTaskAction(
TaskActions.ASSIGN,
selectedTask.id,
selectedTask.tokenUuid,
'john.doe'
)
// Complete a task
await updateTaskAction(
TaskActions.COMPLETE,
selectedTask.id,
selectedTask.tokenUuid
)
updateBulkTaskAction
Applies an action to multiple tasks at once.
await updateBulkTaskAction(
action,
taskIds,
options
)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
action | The action to execute | ExecuteTaskActions | ✅ | TaskActions.COMPLETE |
taskIds | Array of task IDs | string[] | ✅ | ["task-1", "task-2"] |
options | Additional options | object | ❌ | { username: "john.doe" } |
await updateBulkTaskAction(
TaskActions.COMPLETE,
['task-1', 'task-2', 'task-3']
)
updateTaskPriority
Updates the priority of a specific task.
await updateTaskPriority(taskId, priority)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
priority | New priority value | number | ✅ | 5 |
await updateTaskPriority(selectedTask.id, 10)
await saveComment(taskId, commentData)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
commentData | Comment data object | object | ✅ | { message: "New comment text" } |
await saveComment(selectedTask.id, {
message: 'This task requires immediate attention'
})
// Refresh comments after saving
const updatedComments = await fetchTaskComments(selectedTask.id)
await removeComment(taskId, commentId)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
taskId | The unique task ID | string | ✅ | "task-123" |
commentId | The unique comment ID | string | ✅ | "comment-456" |
await removeComment(selectedTask.id, comment.commentId)
Enumerations
getEnumerationOptions
Retrieves enumeration options for a specific enumeration name.
const options = await getEnumerationOptions(enumName)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
enumName | The enumeration name | string | ✅ | "Status" |
TaskManagerEnumeration objects.
Real-time Updates (SSE)
initSseConnection
Initializes a Server-Sent Events (SSE) connection for real-time task updates.
const sseConnection = initSseConnection(
resourceId,
eventHandler
)
| Name | Description | Type | Mandatory | Example |
|---|
resourceId | The resource ID from the view | string | ✅ | "resource-123" |
eventHandler | Callback function to handle SSE events | (event: MessageEvent<string>, data: SseEventData | null) => void | ✅ | See example below |
SseConnection object with a close() method.
Example:
const handleSseEvent = (event: MessageEvent<string>, eventData: SseEventData | null) => {
if (event.type === SseMessageType.Data) {
if (eventData?.eventType === SseTaskMessageType.VIEW_UPDATED) {
// Reload tasks when view is updated
loadTasks()
}
}
}
const sseConnection = initSseConnection(view.resourceId, handleSseEvent)
// Cleanup on component unmount
useEffect(() => {
return () => {
if (sseConnection) {
sseConnection.close()
}
}
}, [])
SseTaskMessageType.VIEW_UPDATED - View configuration has been updatedSseTaskMessageType.TASK_CREATED - A new task has been createdSseTaskMessageType.TASK_UPDATED - A task has been updatedSseTaskMessageType.TASK_DELETED - A task has been deleted
Custom CSS
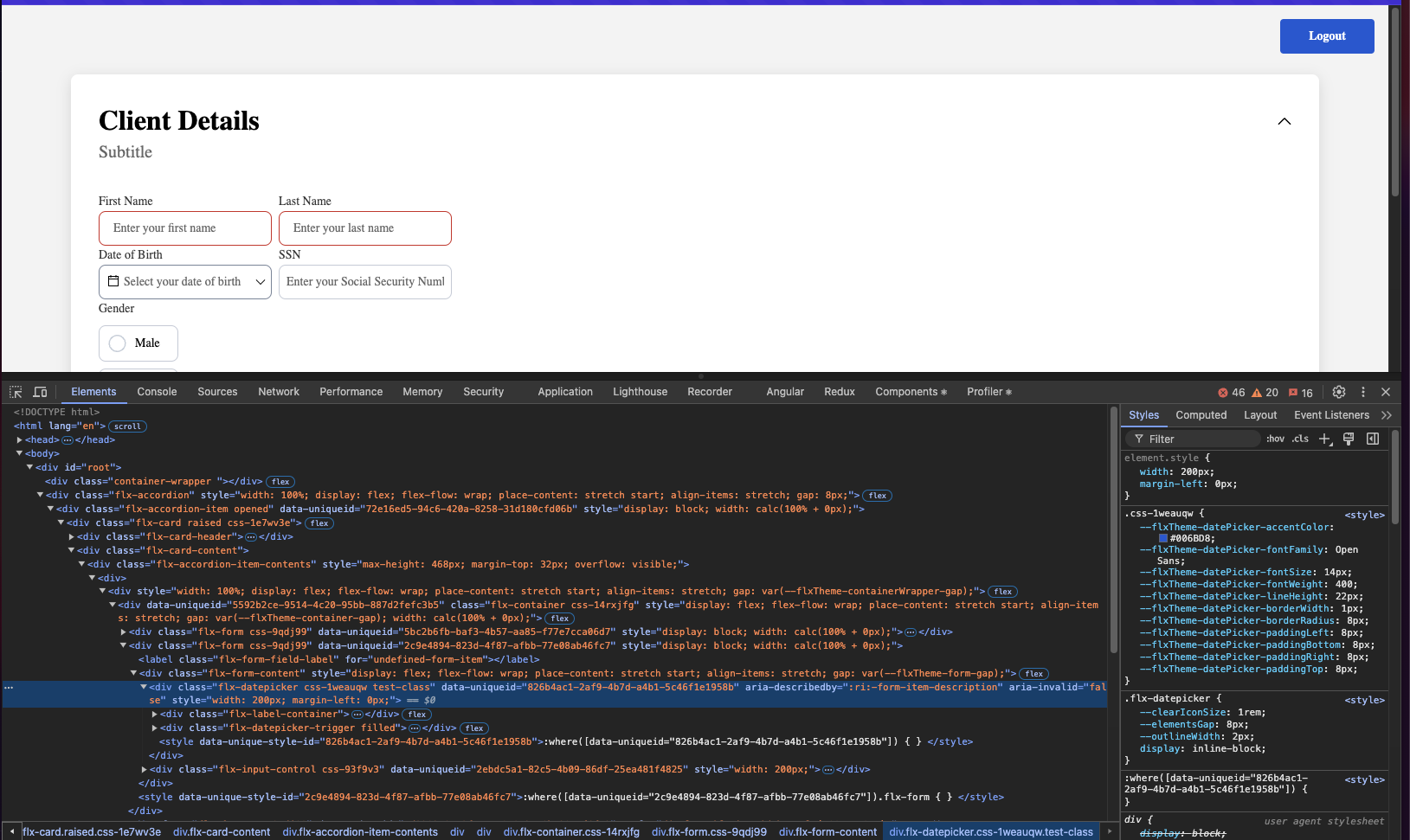
The renderer SDK allows you to pass custom CSS classes on any component inside the process. These classes are then applied to the component’s root element.
To add a CSS custom class to a component, you need to define the class in the process designer by navigating to the styles tab of the component, expanding the Advanced accordion and writing down the CSS class.
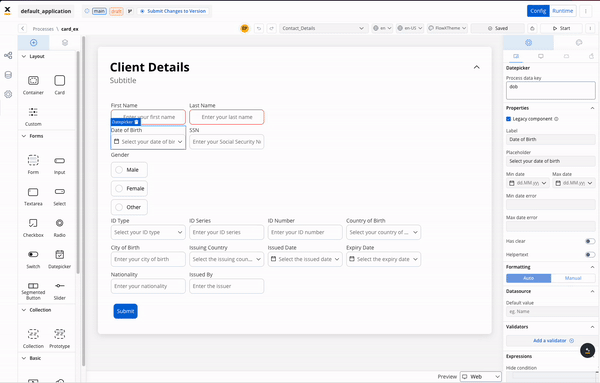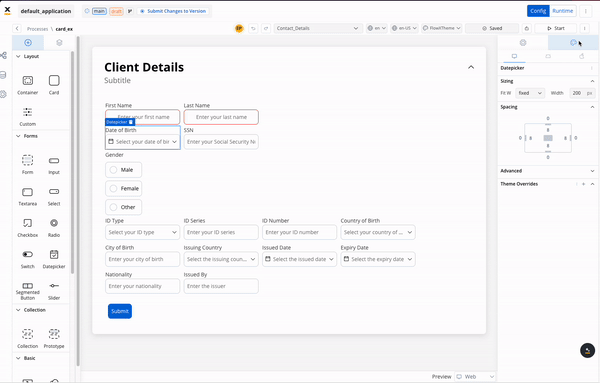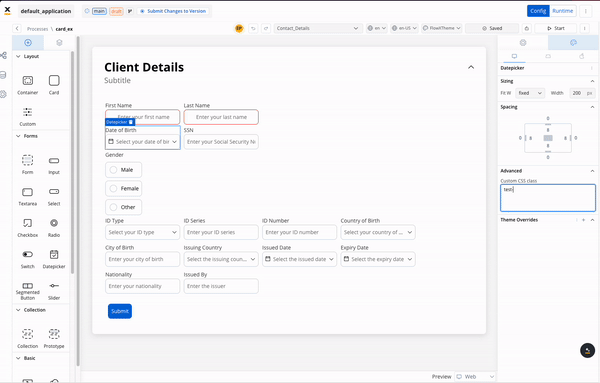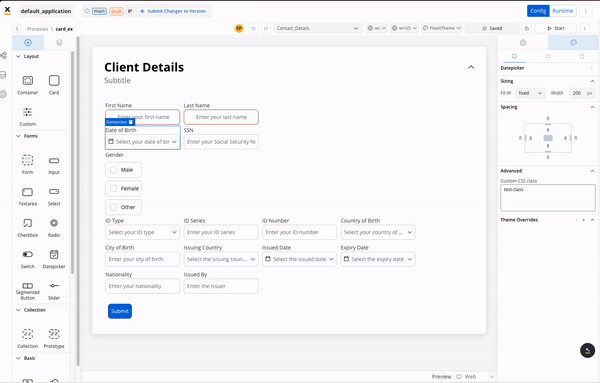
The classes will be applied last on the element, so they will override the classes already defined on the element.
Storybook
Below you find a Storybook which demonstrates how components behave under different states, props, and conditions, it allows you to preview and interact with individual UI components in isolation, without the need for a full-fledged application:


 The properties that can be configured are as follows:
The properties that can be configured are as follows: